Cannabigerol (CBG)
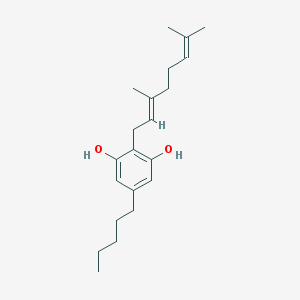
Molecular Formula: C21H32O2
Image credit: PubChem
CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid. CBG can activate α2-adrenoceptors, bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors and block CB1 and 5-HT1A receptors.
Evidence that the plant cannabinoid cannabigerol is a highly potent α2-adrenoceptor agonist and moderately potent 5HT1A receptor antagonist
Cascio M, Gauson L, Stevenson L, Ross R, Pertwee R.
British Journal of Pharmacology. 2010;159(1):129-141.
doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00515.x.
PMCID: PMC2823359
CBG interacts with specific targets involved in carcinogenesis. CBG blocks transient receptor potential (TRP) M8 (TRPM8), activates TRPA1, TRPV1 and TRPV2 channels, blocks 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A (5-HT1A) receptors and inhibits the reuptake of endocannabinoids.
Colon carcinogenesis is inhibited by the TRPM8 antagonist cannabigerol, a Cannabis-derived non-psychotropic cannabinoid.
Borrelli F, Pagano E, Romano B, Panzera S, Maiello F, Coppola D, De Petrocellis L, Buono L, Orlando P, Izzo AA.
Carcinogenesis. 2014 Dec;35(12):2787-97. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu205. Epub 2014 Sep 30.
PMID: 25269802
In vivo, CBG inhibited the growth of xenograft tumors as well as chemically-induced colon carcinogenesis. CBG hampers colon cancer progression in vivo and selectively inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells, an effect shared by other TRPM8 antagonists.
Further reading
ChemIDplus #25654-31-3
ChemSpider #4474921
WikiPedia
ChEMBL #497318
ZINC #04217650